
The seismic survey is one form of the geophysical survey that aims at measuring the earth’s (geo-) properties by means of physical (-physics) principles such as magnetic,
electric, gravitational, thermal, and elastic theories. It is based on the theory of elasticity and therefore tries to deduce elastic properties of materials by measuring their
response to elastic disturbances called seismic (or elastic) waves.
What Are Seismic Waves?
electric, gravitational, thermal, and elastic theories. It is based on the theory of elasticity and therefore tries to deduce elastic properties of materials by measuring their
response to elastic disturbances called seismic (or elastic) waves.
What Are Seismic Waves?
A seismic source such as sledgehammer is used to generate seismic waves, sensed by
receivers deployed along a preset geometry (called receiver array), and then recorded by
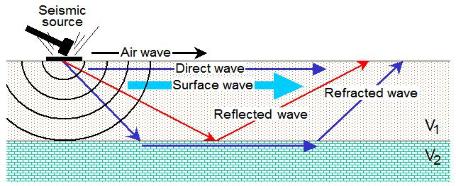
a digital device called seismograph (Fig. 1). Based on typical propagation mechanism
used a seismic survey, seismic waves are grouped primarily into direct, reflected,
refracted, and surface waves (Fig. 2).
The seismic survey consists of three major types: refraction, reflection, and surface-wave
surveys depending on the specific type of waves being used. Each type of seismic survey
method utilizes a specific type of waves (for example, reflected waves for reflection
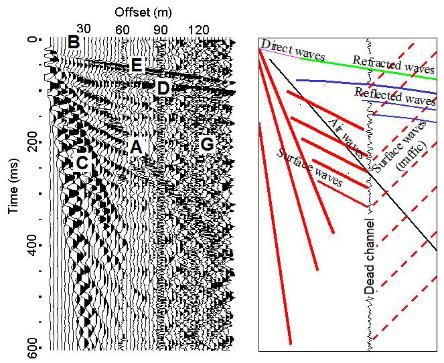
survey) and its specific arrival pattern on a multichannel record (Fig. 3). Seismic waves
used for the survey can be generated in two ways: actively or passively. They can be
generated actively by using an impact source like sledgehammer or passively by natural
(for example, tidal motion and thunder) and cultural (for example, traffic) activities. Most of
the seismic surveys historically implemented have been the active type. Seismic waves
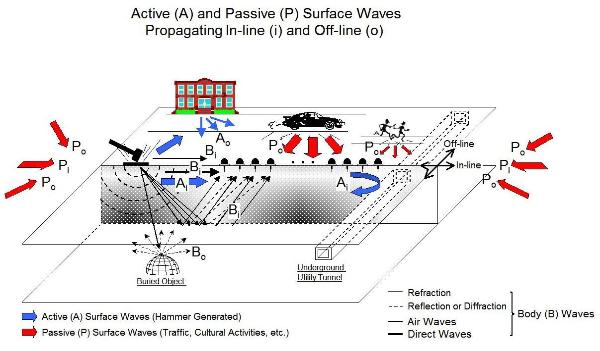
propagating within the vertical plane holding both source and receivers are also called
inline waves, whereas those coming off the plane are called offline waves (Fig. 4).
Refraction Survey Reflection Survey Surface-Wave Survey
receivers deployed along a preset geometry (called receiver array), and then recorded by
a digital device called seismograph (Fig. 1). Based on typical propagation mechanism
used a seismic survey, seismic waves are grouped primarily into direct, reflected,
refracted, and surface waves (Fig. 2).
The seismic survey consists of three major types: refraction, reflection, and surface-wave
surveys depending on the specific type of waves being used. Each type of seismic survey
method utilizes a specific type of waves (for example, reflected waves for reflection
survey) and its specific arrival pattern on a multichannel record (Fig. 3). Seismic waves
used for the survey can be generated in two ways: actively or passively. They can be
generated actively by using an impact source like sledgehammer or passively by natural
(for example, tidal motion and thunder) and cultural (for example, traffic) activities. Most of
the seismic surveys historically implemented have been the active type. Seismic waves
propagating within the vertical plane holding both source and receivers are also called
inline waves, whereas those coming off the plane are called offline waves (Fig. 4).
Refraction Survey Reflection Survey Surface-Wave Survey
| Fig. 1. Schematic of overall field setup for a seismic survey. |
| Fig. 2. Major types of seismic waves based on propagation characteristics. |
Fig. 3. (Right) A field record and interpretation of different seismic events based on
the arrival pattern. Fig. 4. (Below) Illustration of active versus passive waves and
inline versus offline waves.
the arrival pattern. Fig. 4. (Below) Illustration of active versus passive waves and
inline versus offline waves.
What is seismic survey?